
Une technologie unique, démontrée par des milliers d'études scientifiques
- Plus de 125 000 études scientifiques*
- 50 années de recul et d’expérience cumulée
- Pour la première fois miniaturisé et optimisé
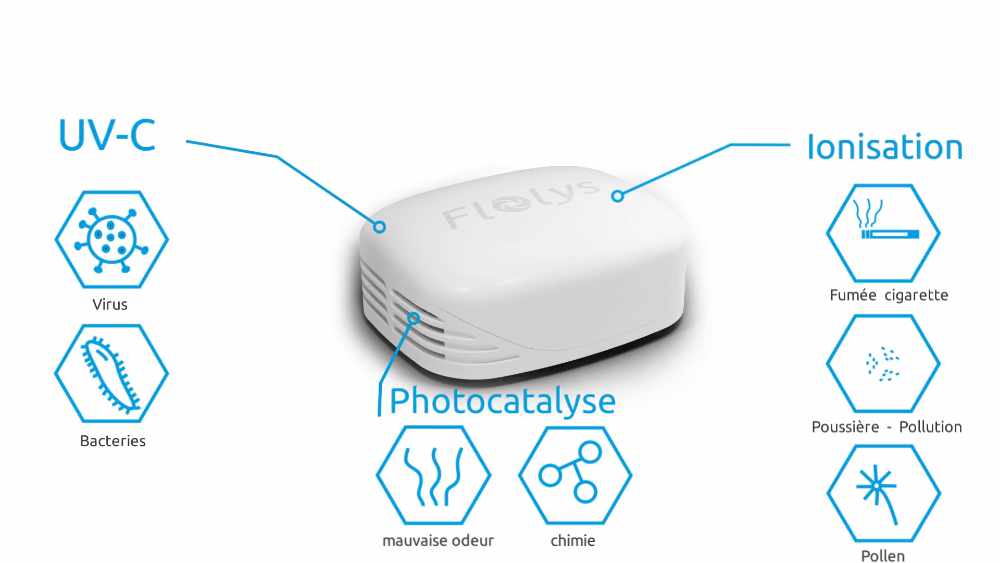


Étudiée depuis plusieurs décennies, elle est considérée comme l’une des méthodes les plus prometteuses pour la purification de l’air dans les bureaux, les usines, les domiciles particuliers ou collectifs, les voitures et les moyens de transport collectifs. Cette technologie est capable de détruire la plupart des contaminants organiques et polluants chimiques, tels que l’éthanol, l’acétaldéhyde, l’acide acétique, le formaldéhyde et l’acide formique6.
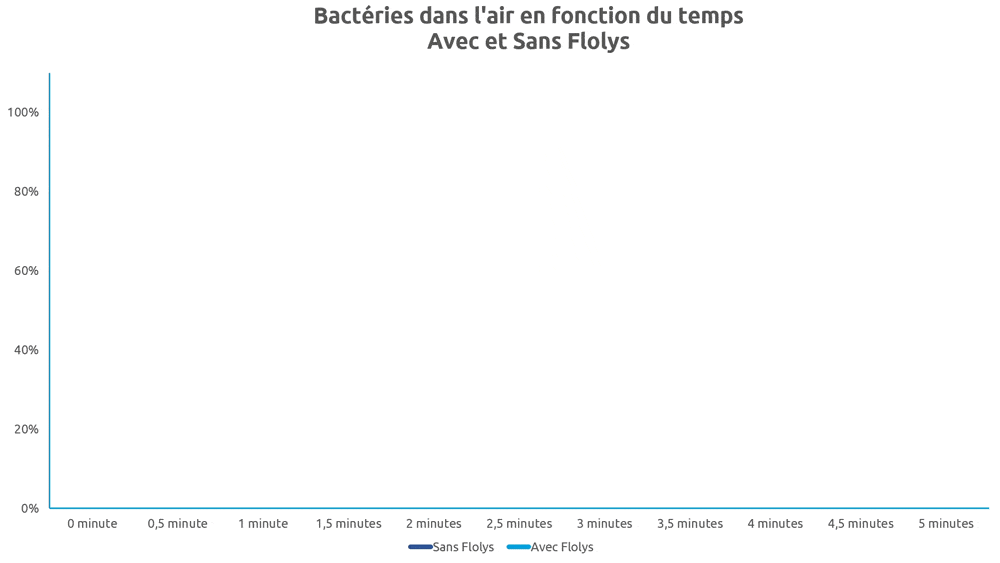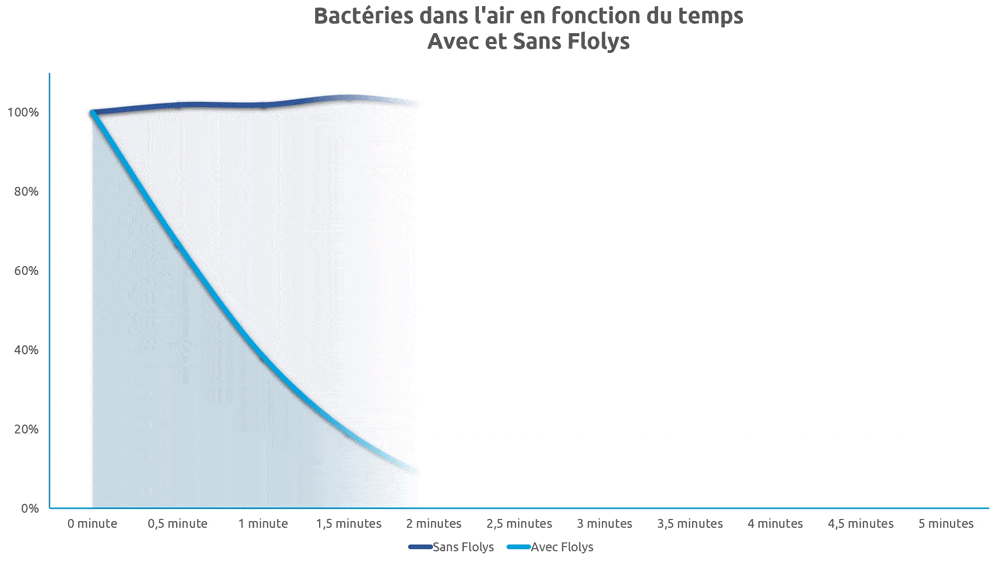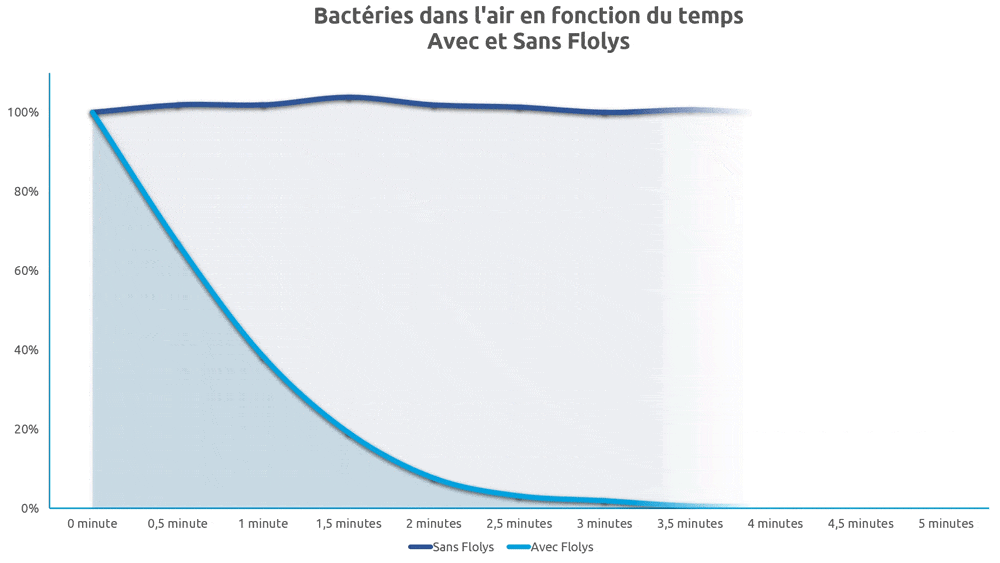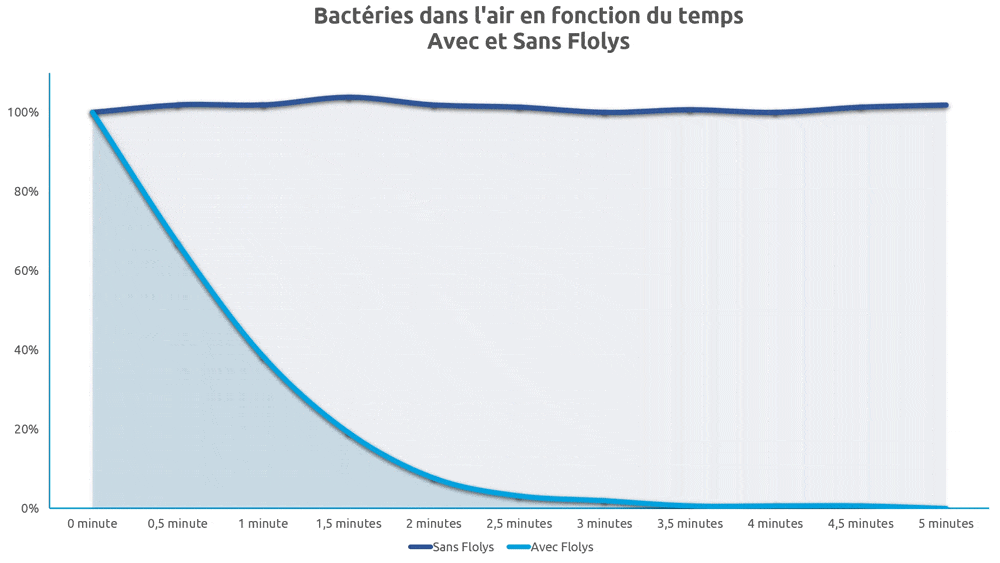
On assiste à un effet de purification très pertinent pour les domaines de la microbiologie, l’hygiène médicale, la lutte antibactérienne, antivirale et fongicide7,8. Hajkova et al.9 ont notamment démontré la capacité de la photocatalyse à éliminer totalement des colonies d’Escherichia Coli.
Modifie la charge électrostatique des particules fines de l’air, ce qui les force à tomber au sol et les y « emprisonne ». Ces particules sont dès lors incapables d’agresser vos voies respiratoires.
Tanaka et al. ont rapporté que l’ionisation réduisait de 46 % le nombre de poussières respirables et inhalables10. La concentration de particules a été réduite de deux ordres de grandeur après deux heures de traitement par ionisation dans un bureau de 50 m3(11). De nombreux autres rapports similaires complètent ces résultats, quant à l’efficacité de l’ionisation dans l’élimination des particules fines12–21, et notamment des microparticules présentes dans la fumée de cigarette16.
Constitue une excellente solution de désinfection et décontamination, et présente l’avantage d’être une stratégie de décontamination sans consommables.
Dans une étude sur le pouvoir décontaminant des UVc sur plusieurs centaines de souches pathogènes connues, Malayeri et al.1 ont montré que toutes les bactéries et tous les virus exposés au UVc sont détruits par ces derniers, y compris les coronavirus SARS-COV2 et MERS-COV3. Les longueurs d’onde les plus efficaces contre les coronavirus se trouvent entre 254 et 270 nm4,5.
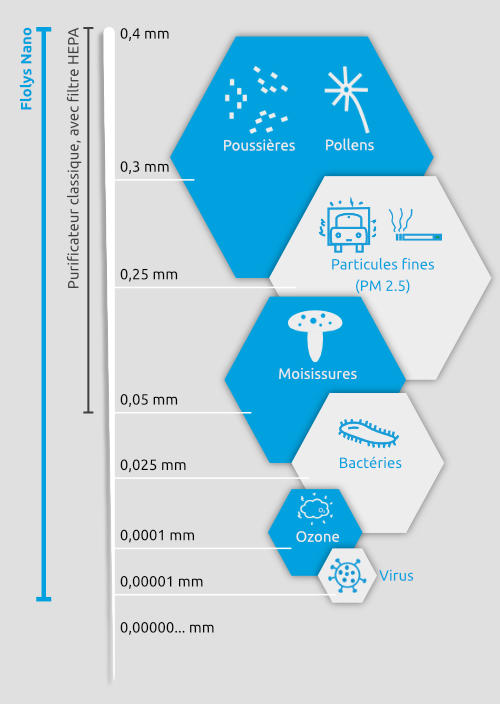
Contrairement aux filtres HEPA (technologie utilisée par les purificateurs conventionnels) qui ne peuvent pas filtrer les particules les plus petites, l’efficacité de notre technologie Aero-Pure n’a aucune limite.
De plus, Flolys Nano ne se contente pas d’accumuler les polluants au même endroit (filtre), mais les élimine réellement.
En continuant à utiliser ce site, vous acceptez les conditions générales et notre utilisation des cookies. Ignorer